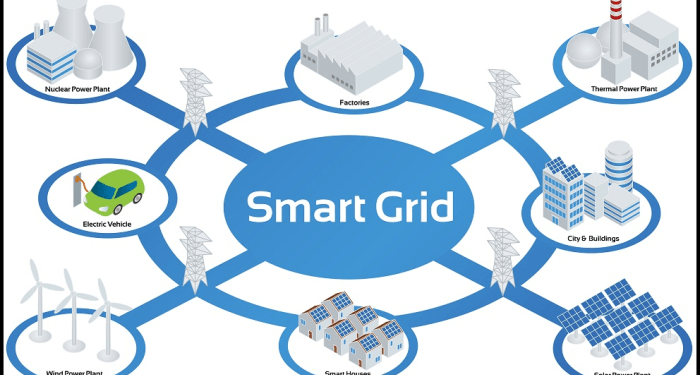
With Smart grid technology for electric power distribution at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling filled with unexpected twists and insights. Smart grid technology is revolutionizing the way we manage and distribute electricity, paving the way for a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable energy future.
Exploring the key components and benefits of smart grid technology sheds light on its transformative impact on the power distribution landscape.
Overview of Smart Grid Technology
Smart grid technology refers to modernizing the traditional electric power distribution system by incorporating advanced digital communication and monitoring capabilities. This allows for more efficient and reliable electricity transmission and distribution.
Definition of Smart Grid Technology
In the context of electric power distribution, smart grid technology involves the use of digital communication and automation to monitor and control the flow of electricity. It enables two-way communication between utilities and consumers, facilitating real-time adjustments to meet demand and optimize energy usage.
Main Objectives of Implementing Smart Grid Technology
- Enhancing reliability and resilience of the power grid.
- Improving energy efficiency and reducing waste.
- Integrating renewable energy sources effectively.
- Empowering consumers with real-time data and control over their energy usage.
Key Features and Components of a Smart Grid System
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) for real-time data collection.
- Distribution Management Systems (DMS) for automated monitoring and control.
- Energy Storage Systems for better integration of renewable energy.
- Smart Sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) devices for improved grid visibility and management.
Examples of How Smart Grid Technology Improves Efficiency in Power Distribution
- Dynamic pricing based on real-time demand, encouraging off-peak usage and reducing strain on the grid.
- Remote monitoring and control of electricity flow, enabling quicker response to outages and minimizing downtime.
- Integration of electric vehicles with the grid, allowing for smart charging and balancing of energy demand.
Benefits of Smart Grid Technology
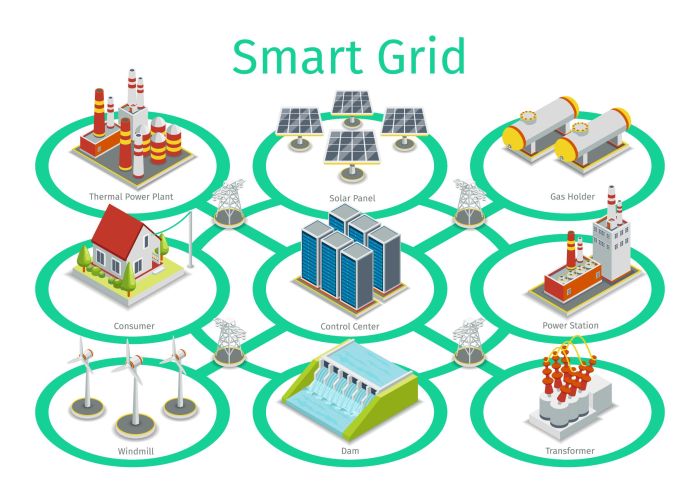
Smart grid technology offers numerous advantages in electric power distribution, revolutionizing the way we manage and consume electricity. By integrating advanced communication and monitoring systems, smart grid technology enhances efficiency, reliability, and sustainability in the power grid.
Enhanced Efficiency
Smart grid technology enables real-time monitoring and control of electricity flow, optimizing energy distribution and reducing wastage. By incorporating sensors and automated systems, smart grids can detect and address issues promptly, ensuring efficient energy usage.
Improved Reliability and Resilience
In comparison to traditional power distribution systems, smart grids are more resilient to disruptions and outages. Through self-healing capabilities and decentralized energy generation, smart grids can quickly adapt to changes and maintain a reliable power supply even during emergencies.
Promotion of Sustainability
Smart grid technology plays a crucial role in promoting sustainability by facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources. By enabling the efficient integration of solar, wind, and other clean energy sources into the grid, smart grids contribute to reducing carbon emissions and fostering a greener energy landscape.
Cost Savings
Smart grid technology helps utilities and consumers save costs through optimized energy management. By implementing demand response programs and dynamic pricing, smart grids encourage energy conservation and reduce overall electricity expenses for both providers and users.
Data-driven Decision Making
Smart grid technology utilizes data analytics to provide valuable insights for decision-making processes. By analyzing consumption patterns and grid performance data, utilities can make informed decisions to enhance operational efficiency, plan for future energy needs, and address potential issues proactively.
Components of a Smart Grid System
Smart grid technology relies on a variety of components to optimize power distribution, improve efficiency, and integrate renewable energy sources seamlessly.
Sensors
Sensors play a crucial role in a smart grid system by collecting real-time data on power usage, grid conditions, and equipment performance. These sensors can detect issues such as outages or fluctuations in power supply, enabling utilities to respond quickly and make necessary adjustments.
Meters
Smart meters are another essential component of a smart grid system. These advanced meters provide detailed information on energy consumption patterns, allowing consumers to monitor their usage more effectively. By integrating smart meters into the grid, utilities can implement demand response programs and encourage energy conservation.
Automation Systems
Automation systems, including advanced control algorithms and communication networks, enable smart grid technology to automatically adjust power flow, reroute electricity, and balance supply and demand in real time. These systems help utilities maintain grid stability, reduce downtime, and optimize energy distribution.
Real-world Examples
One example of how these components work together is in the deployment of smart grid systems in cities like Amsterdam, where sensors, meters, and automation systems are used to monitor energy consumption, detect faults, and manage renewable energy sources efficiently.
By integrating solar panels and wind turbines into the grid, Amsterdam has been able to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
Smart grid technology facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the grid by enabling better control and management of variable energy production. By leveraging sensors, meters, and automation systems, utilities can optimize the use of renewable energy, store excess power, and ensure a stable and reliable energy supply for consumers.
Challenges and Future Trends
Implementing smart grid technology for electric power distribution comes with its own set of challenges. One major challenge is the high initial cost of upgrading existing infrastructure to incorporate smart grid systems. This financial barrier can be a significant hurdle for many utility companies looking to modernize their grids.
Additionally, interoperability issues between different systems and devices can pose challenges in achieving seamless integration within the grid.
Cybersecurity Concerns
Cybersecurity is a major concern when it comes to smart grid systems. As these systems become more interconnected and reliant on digital communication, they become vulnerable to cyber attacks. Ensuring secure communication channels, implementing robust authentication protocols, and regularly updating security measures are essential to safeguarding smart grid technology from potential threats.
Future Trends in Smart Grid Technology Development
The future of smart grid technology is promising, with several trends emerging to shape its development. One such trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to optimize grid operations, improve efficiency, and enhance predictive maintenance.
Another trend is the integration of renewable energy sources and energy storage systems into the grid, allowing for better management of fluctuating energy supply and demand.
Adapting to Changing Energy Demands and Technological Advancements
Smart grid technology is poised to adapt to changing energy demands and advancements in technology by enabling real-time monitoring and control of energy distribution. This flexibility allows the grid to dynamically respond to changes in energy supply and demand, integrate new energy sources seamlessly, and support the growing trend towards electrification of transportation.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, Smart grid technology for electric power distribution is not just a concept but a tangible solution to address the evolving energy needs of our society. By embracing this innovative approach, we are taking a significant step towards a greener and more resilient energy infrastructure.
FAQ Insights
What are the main objectives of implementing smart grid technology?
The main objectives include enhancing grid reliability, improving energy efficiency, integrating renewable energy sources, and enabling better demand response.
How does smart grid technology enhance reliability and resilience in the power grid?
Smart grid technology allows for real-time monitoring, quick detection of faults, and automatic rerouting of power, improving grid reliability and resilience to outages.
What challenges are faced in implementing smart grid technology for electric power distribution?
Challenges include high initial costs, interoperability issues with legacy systems, cybersecurity concerns, and the need for regulatory frameworks to support grid modernization.
How can smart grid technology adapt to changing energy demands and advancements in technology?
Smart grid technology can adapt by incorporating advanced analytics, machine learning algorithms, and grid optimization tools to dynamically manage energy loads and integrate new technologies seamlessly.