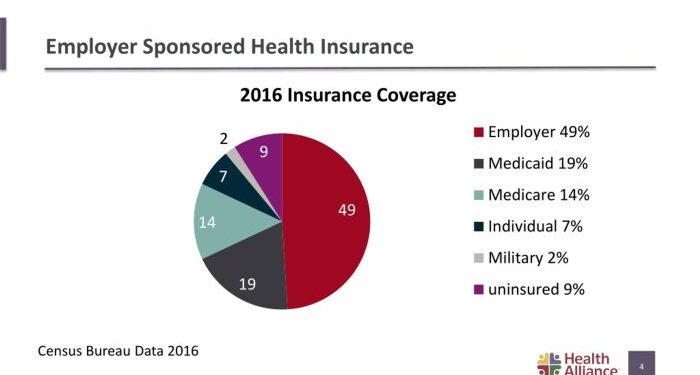
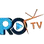Employer-sponsored health benefits worldwide set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. As we delve into the intricate web of health benefits provided by employers across the globe, a tapestry of diverse practices and trends unfolds before us.
From the evolving landscape of health benefits to the impact of cultural nuances on benefit packages, this exploration promises to shed light on a crucial aspect of employee welfare that transcends geographical boundaries.
Overview of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits Worldwide
Employer-sponsored health benefits refer to medical, dental, vision, and other healthcare-related coverage provided by employers to their employees. These benefits are a crucial part of the overall compensation package offered by companies around the world.In different countries, the significance of employer-sponsored health benefits varies based on the healthcare system in place.
For example, in countries with universal healthcare coverage, these benefits may serve as supplements to the basic healthcare services provided by the government. On the other hand, in countries with predominantly private healthcare systems, employer-sponsored health benefits become essential for employees to access quality healthcare services.Furthermore, the nature of these benefits can vary across industries and sectors globally.
For instance, industries with higher risks of occupational hazards, such as construction or mining, may offer more comprehensive health insurance coverage to ensure the well-being of their workers. Similarly, sectors that require specialized medical services, like technology or finance, may provide additional benefits like mental health support or telemedicine options to meet the unique needs of their employees.
Trends in Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits
Employer-sponsored health benefits have been evolving to adapt to the changing needs and preferences of employees. Let's explore some of the current trends shaping the provision of health benefits by employers and how they are meeting the demands of their workforce.
Employee Preferences Impact
Employers are increasingly taking into account the preferences of their employees when designing health benefit packages. This includes offering more flexibility in benefit choices, such as allowing employees to select from a range of health insurance plans or adding options like telemedicine services.
By catering to the individual needs and preferences of employees, employers can enhance the overall satisfaction and well-being of their workforce.
Traditional vs. Innovative Benefits
Traditional healthcare coverage typically includes medical, dental, and vision insurance, along with basic wellness programs. However, in recent years, employers have been introducing innovative benefits to attract and retain top talent. These may include mental health support, alternative therapies like acupuncture or chiropractic care, and even perks like fitness memberships or healthy meal deliveries.
By offering a wider range of benefits, employers can differentiate themselves in a competitive job market and promote a healthier and more engaged workforce.
Global Comparison of Health Benefits Packages
Employer-sponsored health benefits vary considerably across different regions of the world, with unique offerings tailored to meet the needs of diverse workforces. Cultural differences play a significant role in shaping the design of health benefit plans, reflecting the values and priorities of each region.
Let's explore the differences and unique offerings in health benefits packages worldwide.
North America
In North America, health benefit packages often include comprehensive medical coverage, dental and vision benefits, and mental health support. Employers may also provide wellness programs, employee assistance programs, and access to telemedicine services. Health savings accounts (HSAs) and flexible spending accounts (FSAs) are commonly offered to help employees manage healthcare expenses.
Europe
Health benefits in Europe typically encompass universal healthcare coverage, which is funded through social insurance systems or taxation. Employers may offer supplemental health insurance to cover services not included in the public healthcare system. Wellness initiatives, such as gym memberships and mental health support, are also common additions to health benefit packages in Europe.
Asia
In Asia, health benefit packages often emphasize preventative care and wellness programs to promote employee health and productivity. Traditional medicine coverage, such as acupuncture or herbal remedies, may be included in health benefit plans. Some employers in Asia provide access to onsite clinics, health screenings, and mindfulness programs to support employee well-being.
Cost and ROI of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits
Employer-sponsored health benefits come with a significant cost implication for companies operating worldwide. Providing comprehensive health coverage to employees can be expensive, especially in regions where healthcare costs are high. Companies need to carefully consider the financial impact of offering these benefits while still prioritizing the well-being of their workforce
Cost Implications for Employers Offering Health Benefits Worldwide
Employers offering health benefits worldwide must navigate varying healthcare systems, regulations, and costs across different countries. The cost of providing health benefits can differ greatly depending on the location, with some countries having more expensive healthcare services than others. Factors such as the size of the workforce, the level of coverage, and the prevalence of chronic conditions among employees can also impact the overall cost.
- Employers need to account for premiums, deductibles, co-pays, and other out-of-pocket expenses when budgeting for health benefits.
- International companies may face additional challenges such as currency fluctuations and compliance with local healthcare laws.
- Cost-sharing arrangements between employers and employees can help mitigate some of the financial burdens associated with health benefits.
Measuring the Return on Investment (ROI) of Health Benefits
Companies measure the ROI of their health benefits programs by evaluating various metrics such as employee productivity, absenteeism rates, healthcare utilization, and overall employee satisfaction. By tracking these key performance indicators, employers can assess the effectiveness of their health benefits in improving employee well-being and performance.
Calculating the ROI of health benefits involves analyzing both the direct cost savings, such as reduced healthcare expenses, and the indirect benefits, such as improved employee morale and retention.
Strategies to Manage Rising Costs of Health Benefits
To manage the rising costs of health benefits, companies employ various strategies aimed at controlling expenses while maintaining quality coverage for employees. These strategies may include negotiating lower rates with healthcare providers, implementing wellness programs to promote preventive care, and offering telemedicine services to reduce unnecessary medical visits.
- Implementing wellness initiatives can help employees adopt healthier lifestyles, leading to reduced healthcare costs in the long run.
- Leveraging technology solutions like telemedicine can provide cost-effective healthcare options for employees, especially in remote or underserved areas.
- Regularly reviewing and optimizing health benefits plans can help companies stay competitive in the global market while managing costs efficiently.
Compliance and Regulations in Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits
Employer-sponsored health benefits are subject to various regulatory requirements globally, which govern the provision of healthcare coverage by companies to their employees. Ensuring compliance with these regulations poses a significant challenge for organizations operating in multiple countries due to the diverse nature of healthcare laws and policies.
Global Regulatory Landscape
Companies face the complex task of navigating different healthcare regulations across various jurisdictions. From mandatory coverage requirements to tax implications, the regulatory landscape for employer-sponsored health benefits can vary significantly from one country to another.
Challenges in Compliance
- Understanding and interpreting diverse regulations: Companies must stay abreast of the latest healthcare laws and policies in each country where they operate to ensure compliance.
- Managing data privacy and security: With sensitive employee health information involved, companies must adhere to strict data protection regulations to safeguard confidentiality.
- Dealing with changing regulations: Healthcare laws are constantly evolving, requiring companies to adapt their health benefit programs to remain compliant.
Best Practices for Compliance
- Centralized compliance management: Establishing a centralized team or system to oversee compliance efforts can help streamline processes and ensure consistency.
- Regular compliance audits: Conducting periodic audits to assess adherence to regulations and identify any potential areas of non-compliance can help mitigate risks.
- Engagement with legal experts: Seeking guidance from legal professionals well-versed in healthcare regulations can provide valuable insights and ensure compliance with the law.
Last Recap
In conclusion, the realm of employer-sponsored health benefits worldwide is a dynamic ecosystem shaped by myriad factors and considerations. As companies navigate the complexities of providing healthcare coverage to their employees on a global scale, the importance of understanding regional variations and emerging trends cannot be overstated.
This discussion serves as a window into a world where employee well-being intersects with corporate strategies, fostering a dialogue that is both enlightening and thought-provoking.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key differences between health benefit packages in North America and Asia?
In North America, health benefits often include comprehensive coverage for medical services, while in Asia, there may be a greater emphasis on preventive care and wellness programs.
How do companies measure the return on investment (ROI) of employer-sponsored health benefits?
Companies typically assess ROI by tracking metrics such as reduced absenteeism, improved productivity, and employee satisfaction levels.
What are some common challenges companies face in complying with healthcare regulations globally?
Companies often struggle with navigating diverse regulatory requirements, ensuring data privacy compliance, and addressing legal complexities in different countries.